Table of Contents
Key Facts & Summary for Atomic Structure and Periodic Table:
- The particles constituting an atom are the electron, the proton, and the neutron.
- An atom is composed of two regions: the nucleus, which is in the center of the atom and contains protons and neutrons, and the outer region of the atom, which holds its electrons in orbit around the nucleus.
- Protons and neutrons have approximately the same mass, about 1.67 × 10-24 grams, which scientists define as one atomic mass unit (amu) or one Dalton.
- Each electron has a negative charge (-1) equal to the positive charge of a proton (+1).
- Neutrons are uncharged particles found within the nucleus.
- The periodic table is a table that logically organize all the known elements.
- Each row is named “period” where all of the elements have the same number of atomic orbitals.
- Each column is called “group” where the elements have the same number of electrons in the outer orbital.
- Keep reading for more atomic structure and periodic table facts
Every form of matter, or solid, or liquid, or gas, contains atoms.
Every atom has a basic nucleus at the center, consisting of a certain number of protons and neutrons. The number of this particles are different for different elements. Around the nucleus there is certain number of electrons in fixed orbits, at fixed energy levels.
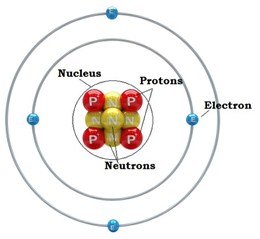
The electron is by far the smallest: At 9.11 x 10-31 kg. It carries a negative electrical charge. Usually, it is bound to the positively charged nucleus due to the attraction created from the opposite electric charges. If the electrons carried by an atom are more or fewer than its atomic number, then the atom becomes respectively negatively or positively charged. A charged atom is known as an ion.
Most of the mass of the atom comes from the protons and neutrons themselves, whereas electrons are almost 1/1837th times the weight of a proton or neutron. Protons and neutrons are both composed of other particles called quarks and gluons.
The atomic number is the number of protons (equal to the number of electrons in a neutral atom) in the atom and the atomic mass number is the sum of the number of protons and neutrons in the atom. The atomic number (Z) is defined as the number of units of positive charges (protons) in the nucleus. It is the number of protons in the nucleus that determines the chemical properties of an atom.
An atom may gain a positive or negative charge by either losing or gaining electrons respectively. Atoms may attach themselves to each other (of the same type or different type) to form molecules of different compounds, to form matter.
In some atoms, the nucleus can change naturally. Such an atom is radioactive. In nature, there are some elements that are radioactive, like uranium or radium. In labs, scientists can produce radioactivity by bombarding atoms with smaller particles.
The molecular mass of a substance is the sum of the atomic masses of all the atoms in a molecule of the substance. It is therefore the relative mass of molecule expressed in atomic mass units (u).
Isotopes are atoms in a chemical element having different numbers of neutrons than protons and electrons. The atoms in a particular element have the same number of protons and electrons, but can carry varying numbers of neutrons.
As instance, Hydrogen’s atomic number is 1, i.e. its nucleus contains 1 proton. It also has one electron. The Hydrogen atom is neutral since it contains the same number of protons and electrons (as the positive and negative charges cancel each other out).
However, approximately, one hydrogen atom out of 6000 contains a neutron in its nucleus. These atoms are still Hydrogen because they have one proton and one electron; they simply have a neutron that most hydrogen atoms do not carry. Hence, these atoms are called Isotopes.
There’s also an isotope of hydrogen that contains two neutrons. It’s called Tritium, it doesn’t occur naturally on earth, but it can easily be created.
The periodic table
The periodic table is a table that logically organize all the known elements. Each element has a specific location according its atomic structure. Each row and column has specific characteristics.
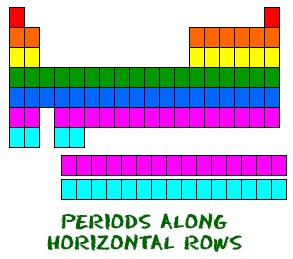
Each row is called a period where all of the elements have the same number of atomic orbitals. For example, every element in the top row (the first period) has one orbital for its electrons. All of the elements in the second row (the second period) have two orbitals for their electrons. As you move down the table, every row adds an orbital. At this time, there is a maximum of seven electron orbitals.
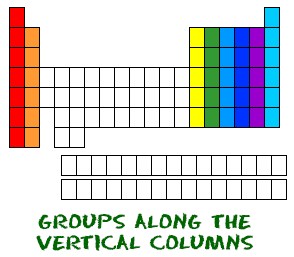
Each column is called a group where the elements have the same number of electrons in the outer orbital. Those outer electrons are also called valence electrons. They are the electrons involved in chemical bonds with other elements. Every element in the first column (group one) has one electron in its outer shell. Every element in the second column (group two) has two electrons in the outer shell.
Hydrogen (H) and helium (He), in its neutral form, does not have a neutron. There is only one electron and one proton. Helium (He) is very stable with only two electrons in its outer orbital (valence shell). Even though it only has two electrons, it is still grouped with the noble gases that have eight electrons in their outermost orbitals, their valence shell is full.
The periodic table can be used also to estimate relatively some other properties of the atoms: electronegativity, ionization energy, electron affinity, atomic radius, melting point, and metallic character. You can use a dynamic periodic table tool to easily refer to specific elements and their atomic number, mass, orbital arrangement, etc.
Read more about atomic symbols and the modern periodic table
Frequently Asked Questions
What are the principal subatomic particles?
The principal subatomic particles are protons, electrons, and neutrons.
What is the difference between protons and neutrons?
Protons and neutrons are subatomic particles residing in the nucleus of an atom. Protons are positively charged, while neutrons are neutral particles.
What is the periodic table?
The periodic table is an arrangement of elements in horizontal rows and vertical groups based on their properties to study them easily.
What is the benefit of the periodic table?
The periodic table helps to study different elements efficiently. Using a periodic table, you can compare the trends of ionization energies, electron affinities, atomic radius, melting point, and metallic character of different elements.
References and further readings:
https://www.toppr.com/bytes/structure-of-atom/
https://www.khanacademy.org/science/chemistry/periodic-table
http://www.rsc.org/periodic-table
https://www.livescience.com/37206-atom-definition.html





