Table of Contents
Key Information & Summary:
- An electrode is an apparatus in which current travels through an object of substance
- Not all metals can conduct electricity in solid state
- Aqueous solutions are used in electrodes
- Electrodes are called half cells
What are electrodes?
Electrodes, also known as half cells, are used to find the Eθ of different elements. They have a beaker with a rod of metal or a platinum wire with platinum black. Platinum black is used when substances are liquid or aqueous to conduct current as it is an inert metal that doesn’t take part in reactions and in powdered form has a great surface area for increase in current flow.
Types of electrodes
Metal-metal ion electrode:
These electrodes are made up of a metal rod in an aqueous solution of its ion.
Metal ion – metal ion electrode:
These are electrodes in which two ions of the same metal are present in the aqueous solution and a platinum black with platinum wire is used to connect it to another half cell.
Non-metal ion – Non-metal ion electrode:
These electrodes have gases in an inverted tube with a chamber for the gas to enter. Platinum black is used again and the solution has an ion of the gas in it. The gas is introduced through the chamber when needed.
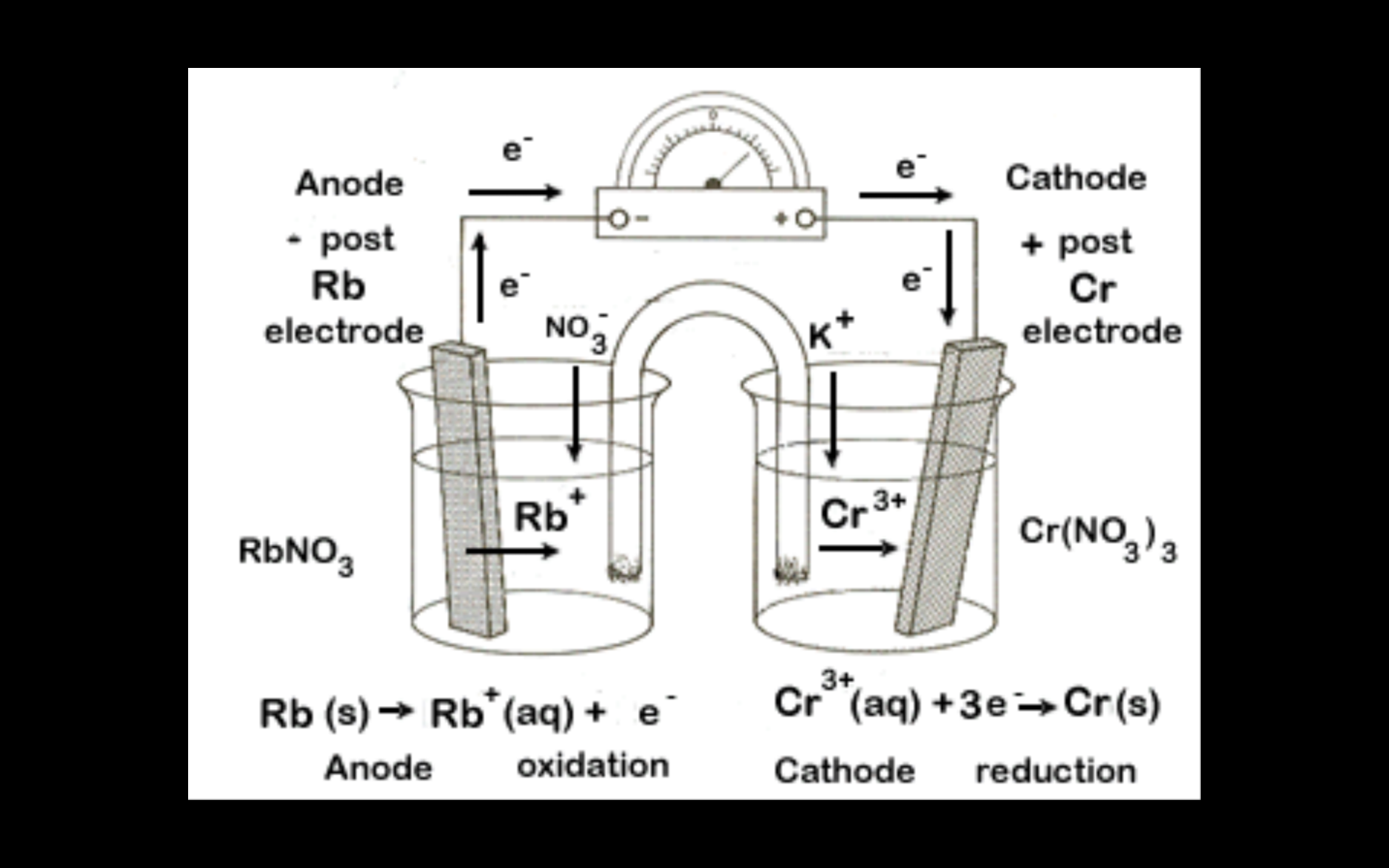
TWO HALF CELLS MAKE A FULL CELL.
Example:
Standard electrode potential
Electrode potential of a half cell compared to standard hydrogen electrode under standard conditions.
STANDARD HYDROGEN ELECTRODE IS USED AS A REFERENCE ELECTRODE, IT IS USED TO MEASURE Eθ VALUE OF OTHER ELECTRODES.
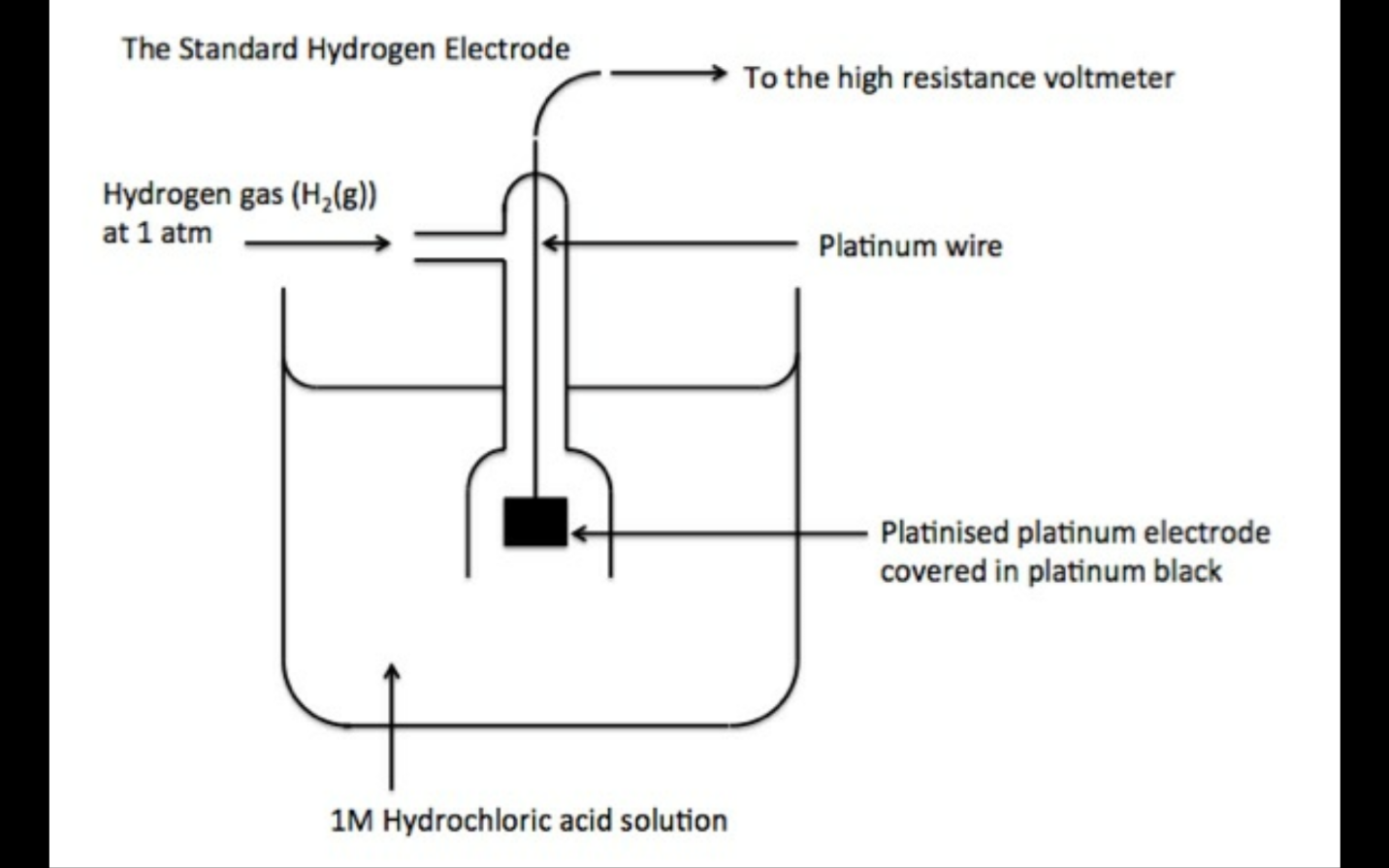
It has an eθ value of 0.0V.
Standard conditions:
Half cells can only work under these conditions:
- The temperature should be 298K
- The pressure should be 1atm
- The concentration of ions should be 100 mol/dm3
Salt bridge:
It is used for completion of an electric circuit. Filter paper soaked in an aqueous solution of KNO3 makes it. Ions move through it.
Note:
Electrons move in external wire
Ions move in solution and salt bridge.
Rules:
- The species on L.H.S is oxidizing agent and the species on R.H.S is reducing agent
- Forward reaction is reduction and backward reaction is oxidation
- Greater Eθ value means oxidizing agent in half cell equation will be stronger and forward reaction will be favoured
- Smaller Eθ value means reducing agent in half cell equation will be stronger and backward reaction will be favoured